Isometric TileMaps
Excalibur can produce isometric style tile maps! Isometric tilemaps, also known as 2.5D, provide a way to draw maps from a simulated 45 degree camera view.
Excalibur has a Tiled plugin to automatically create tilemaps from isometric maps created in the popular Tiled editor. We generally recommend using the plugin, however, read on to understand how isometric tilemaps function in Excalibur.

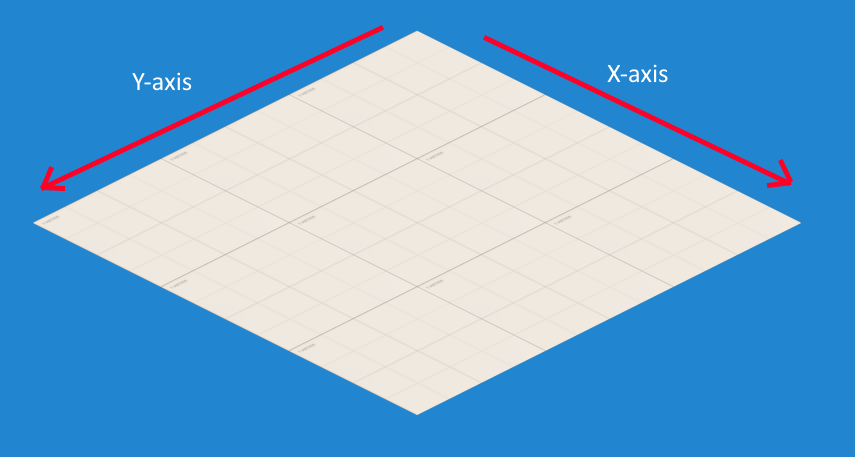
In Excalibur the x-axis moves down the top right edge, and the y-axis moves down the top left edge.
Isometric Map Usage
Use the Excalibur IsometricMap class for drawing isometric grids! (They also support custom colliders via the same mechanism as ex.TileMap)
typescript
typescript
The tilemap is composed of IsometricTile's which are Entities with a IsometricEntityComponent. The IsometricEntityComponent can be applied to any entity that needs to be correctly sorted in the drawing order to preserve the isometric illusion, this is useful if you have players or game objects that move around the map.
The IsometricEntitySystem generates a new z-index based on the elevation and TransformComponent of an entity with IsometricEntityComponent.
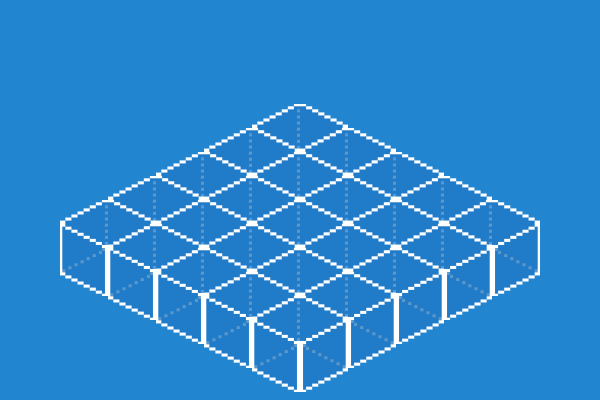
The 5x5 IsometricMap map from the above example snippet will contain 25 IsometricTile's. These are accessible via the tiles property on the IsometricMap instance. e.g. isoMap.tiles. The IsometricMap represents a single layer in an isometric scene.
At this stage the IsometricTile's do not have graphics attached, so they are invisible to the human eye. But the IsometricMap that has been added to the scene can be thought of as:
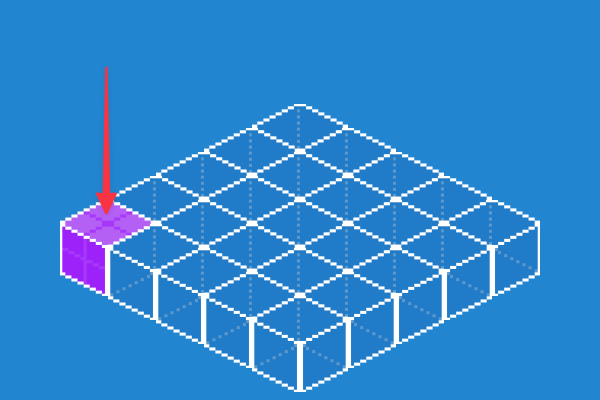
Selecting an appropriate Tile Height
When defining the tileHeight there are a few considerations you should make relative to your asset. Usually the tileHeight is half your graphics total height. With other art assets the tileHeight can be different, in this case roughly half the height of the asset. This height will depend on your art assets.
Converting Coordinates to Tile Coordinates
World space coordinates can be converted to the tile x/y coordinate
typescript
typescript
You can also get the top/left world space coordinate given a tile coordinate.
typescript
typescript
Adding Graphics to IsometricTiles
Graphics can be added to an IsometricTile. Graphics are drawn differently from other parts of Excalibur, they are drawn from the bottom left, this is done to help preserve the illusion of placing tiles on top of a grid.
typescript
typescript
To switch the default behavior and render graphics from the top of a tile, add renderFromTopOfGraphic to the constructor. This can be useful if your Isometric tiles are conceptually "flat" without any perceived height.
typescript
typescript
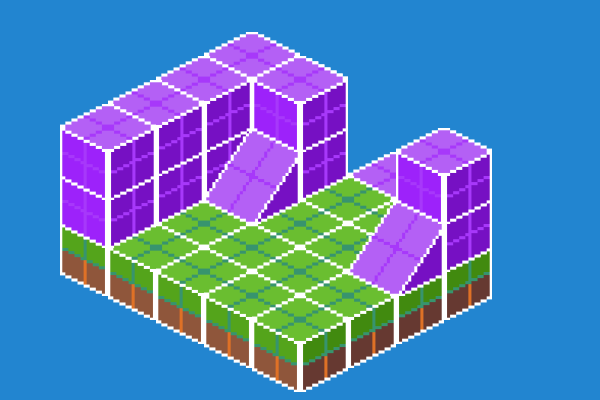
Working with depth and elevation
As noted above, an IsometricMap represents a single layer in an isometric scene. To add some depth to a scene we can "stack" multiple IsometricMap's, adjusting the elevation and y of each subsequent IsometricMap. This will give the desired effect of tiles appearing on top of another.
For more advanced maps, with multiple layers, we recommend using the Tiled plugin which handles the complexity automatically.
typescript
typescript
Adding Colliders to IsometricTiles
Colliders can be added to tiles, colliders are positioned relative to the top left of the tile's asset bounds. You can calculate this by looking at your rectangular tile asset and counting the pixels down from the top left.
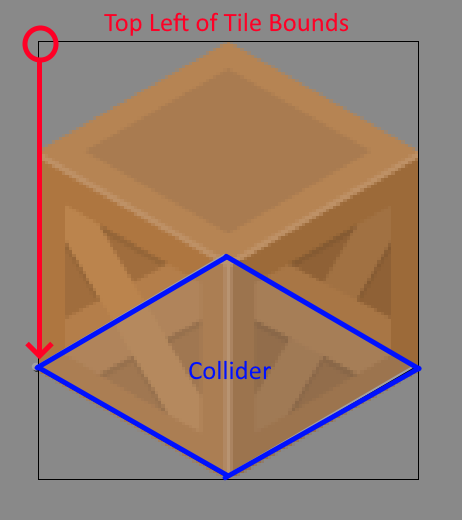
In this example the tile art asset has a width of 111 pixels and a height of 128 pixels.
IsometricTile's need to be set to solid = true for them to act as CollisionType.Fixed colliders.
typescript
typescript
The geometry is shown here in green and the asset graphics bounds are shown in yellow.